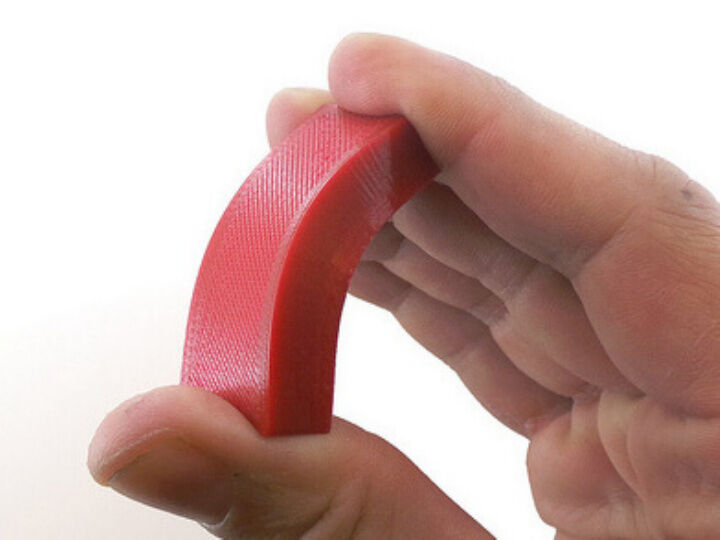
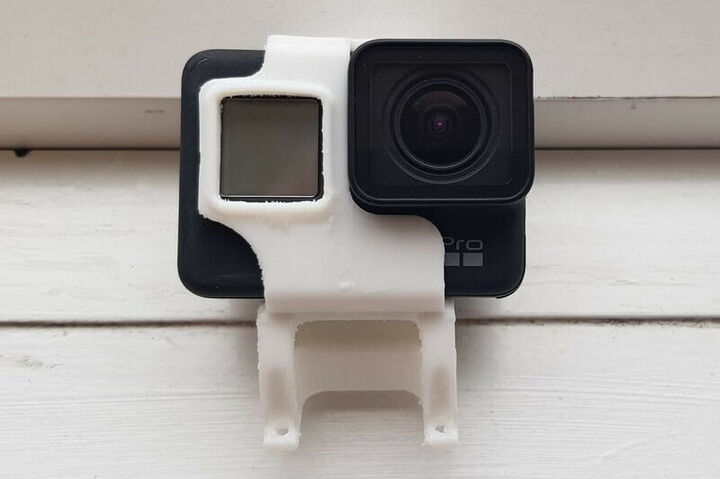
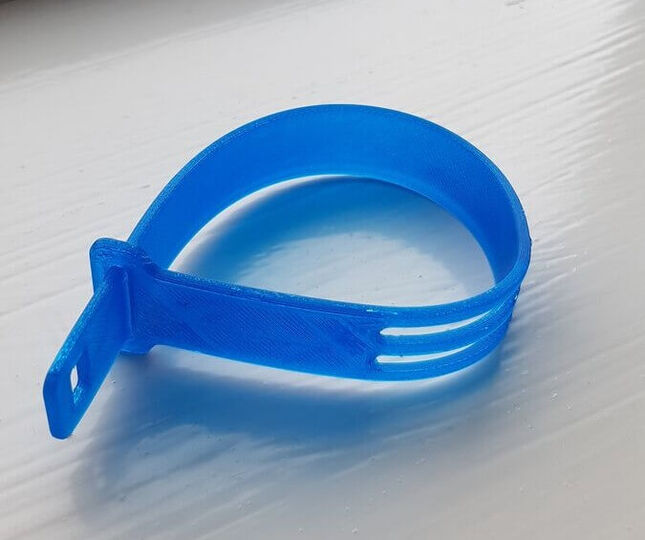



Thermoplastic Polyurethane or TPU is referred to as the bridge between rubbers and plastics. The material appears rubber-like, which means it can be extremely flexible, durable and smooth to the touch. All these properties and compound versatility make TPU widely used in many industries for coatings, components and consumer goods. It is often used for 3D printing.
Order in TPU


| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 5076 psi * |
| Ultimate Elongation | 750% * |
* Value for General Purpose TPU Resin (Shore 70A)
TPU material is a group of thermoplastic elastomers with good elasticity and resistance to stresses like abrasion and oil lubricants. Its structure consists of soft and hard segments linked together in the chain.
The number and character of these segments can vary, resulting in a different material hardness of TPU from soft (Shore 30A) to very hard (Shore 100A), so the material is used both as soft engineering plastic and tough rubber.
TPU is widely used as an additive for strengthening other materials. For example, composites of TPU and Polycarbonate or ABS have an improved flexural modulus up to 150,000 psi. Though pure TPU tensile strength is around 5076 psi (for Shore 70A).
In addition to hardness, TPUs can be manufactured with different base material components. There are three subgroups – polyester, polyether, and polycaprolactone:
Also, TPU can be mixed with specific agents or different proportions of compounds to achieve a certain appearance and features like fire-retardancy, biocompatibility, optical clarity and more.
Clear Silicone and TPU items can turn yellow over time due to chemical reactions when exposed to heat, light and some chemicals. Unfortunately, this aging process is quite common for such materials and once discolored, it can’t be “cleaned” again.
Many goods that have contact with your skin, including clothing or sports items, contain latex - a naturally derived rubber. It can cause allergies and skin irritation (also called hypersensitivity), which makes some people question whether or not TPU may also contain latex.
TPU is a thermoplastic polyurethane and it doesn’t have any agents like mercaptobenzothiazole, thiuram and carbamate (which can be found in latex and cause skin irritation) or latex proteins (that skin absorbs from latex). TPU rubber is a synthetic one, so it has nothing to do with latex. Though it can still cause an allergy if you are sensitive to some synthetic compounds used in a specific TPU blend.
Most of the thermoplastic polyurethane compositions are not biodegradable. However, modern chemical companies offer blends with organic blocks in molecule chains that can degrade in the soil in 3 to 5 years. Though such compounds are usually referred to as Biodegradable TPU to distance them from regular TPU (that is not biodegradable).
TPU can be 3D printed with several technologies to achieve specific properties. FDM printers can melt and extrude TPU filament to create flexible parts like cases, seals, gloves and more. Being flexible, TPU material can cause some difficulties while printing, including jamming, clogging the nozzle and deformation. However, with good calibration and settings, it opens the doors to a large variety of possibilities.
On average, TPU filaments are printed at a high temperature of about 245º+ C (473 °F). Depending on the Shore Hardness of the blend and whether or not there are any additives to it, TPU filament may require different settings.
TPU is actually just a harder grade of TPE (which is Thermoplastic Elastomer). Though for FDM 3D printing it makes some difference. TPE is extremely elastic, which makes it a bit harder to print with - at least with some common extruders.
On top of being harder and, as a result, easier to work with, TPU also has better resistance to abrasion and low temperatures and its shrinks much less than softer TPE. Though these two filaments usually have very different applications.
SLS printers can use TPU based powders to sinter flexible parts as well. Sintered prints have 350% elastic elongation and a long life cycle. There are wider dimensional and constructional possibilities compared to FDM technology, which makes it possible to 3D print bumpers, toys, seals, and footwear components.
Hard grades of TPU like polyamides can be easily machined using common metal and woodworking tools. Punching and thread cutting also works better for this group, however, 0.1 mm clearance for pre-drilled holes should be included into the design. While working with softer grades, the material’s flexibility and elasticity should also be taken into account. This requires using fast steel cutting tools, cooling systems and shavings removal.
TPU exhibits high-performance properties if processed correctly through injection molding. The material is non-abrasive, so a special coating on the tools isn’t necessary. Some manufacturers recommend pre-drying and post-treatment steps for imperfect parts. For molding TPU, the important factors are mold and nozzle temperature, pressure and plasticizing energy. If the molding process or an object’s design doesn’t suit the material, it may cause damage and shrinkage of parts. Despite special conditions required for molding, TPU components are extremely popular in various industries and can be processed with conventional thermoplastic manufacturing equipment.
Cover image by Creative Tools
All Comments (0)