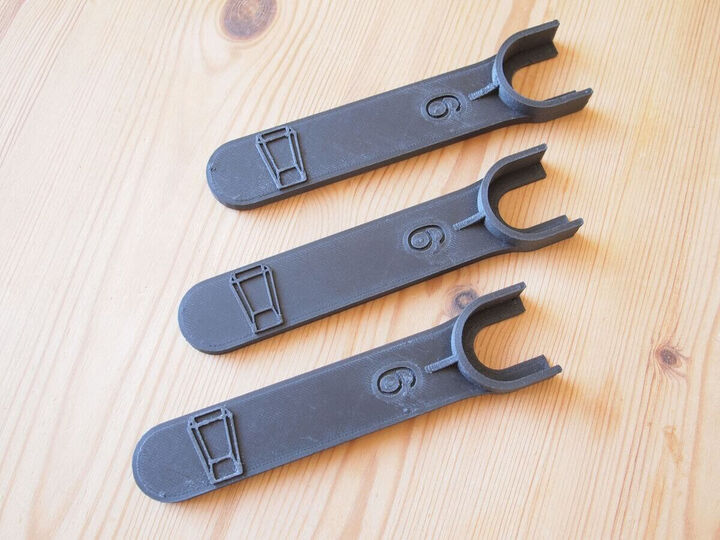
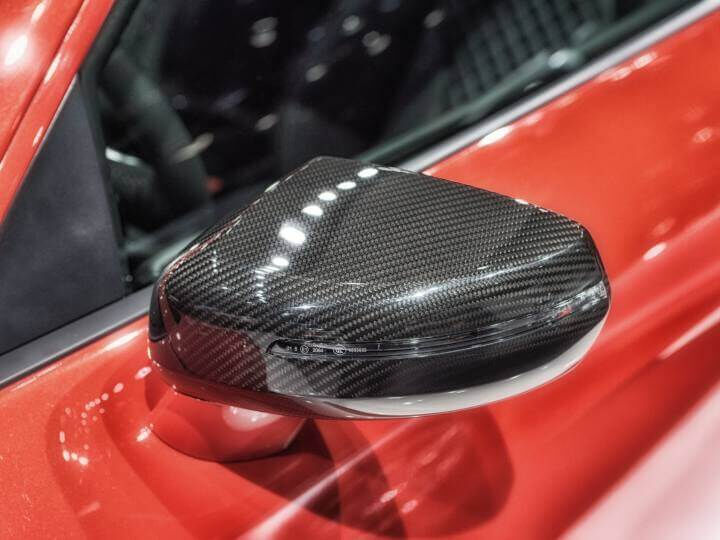



The material known as Carbon Fiber is typically a composite of carbon fibers and a thermoplastic or a thermosetting resin. It’s best known for its incredible strength and durability, making it ideal for engineering, aerospace, sporting goods and more. Aside from professional usage, there are carbon fiber rings, phone cases and jewelry pieces on the market which were inspired by the unique aesthetic appearance of the material. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers, or CFRPs for short, are quite difficult and costly to produce.
Order in Carbon Fiber





Carbon Fibers are thin fibers composed mostly of carbon and manufactured mainly by spinning and carbonizing polymers like polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or petroleum pitch. This is a several step process that includes heating the raw material for long hours in extreme temperatures until all the non-carbon atoms are shed.
The fibers themselves are composed with thermoset resins or polymers to receive a strong, lightweight and resistant material we call Carbon Fiber or Carbon Composite. It appears as a woven structure. There are numerous carbon fiber reinforced materials that feature fibers used with nylons, epoxy, PEEK, and more. Sometimes, other additives like glass, aluminum, aramid and silica can be included into a material as well to improve its performance.
Fibers can be mixed with the matrix material beforehand or just layered one after another in the final product. Different molding methods are commonly used to manufacture parts from CFRPs since the material itself appears more likely as a piece of fabric rather than a block of a material.
“Carbon Fiber” itself appears as a woven material, which is typically pressed into a mold of the product and fixed with the help of resin. However, composites with carbon fiber additives can be processed in other ways too.
Carbon Fiber reinforced filaments can be used in FDM 3D printing. The percentage of carbon fibers in the composites can vary a lot, influencing the weight and strength of the end prints. Typically, fibers are composed with Nylon, ABS, PETG, PLA, and more. Additives influence the printing process, causing the filament to clog more than standard materials, and requires a stronger nozzle and higher temperatures.
Another technology of 3D printing which can produce carbon fiber parts is called Selective Laser Sintering - it uses a powdered composite of carbon fibers and plastic. The prints have a black finish, appear strong and they also preserve conductive properties.
Carbon Fiber materials can be CNC machined or water cut. Waterjet is the recommended method to cut carbon fiber since it doesn’t require special tooling and helps cooling the workpiece. The only potential issue is delamination, which can be easily avoided by starting the process with a hole.
CNC milling can also be used but it would require a higher speed, special tooling and playing with feed rate settings to avoid overheating the piece during the production process. Carbon Fibers are very abrasive for drills and material dust is potentially dangerous to the machine if left in the working area. The conductive particles can catch an electric current and irritate skin as well.
A common way to mold carbon fiber is with the use of CF cloth sheets that can be layered in a form of a part and filled with epoxy to hold together. Alternatively, CF sheets or chopped pieces can be applied over a master model with a release agent on it. Carbon Fiber is then wetted with resin to harden.
Compression molding can be used as well: carbon fiber material and resin would be pressed together between two molds. This technology, however, is typically more expensive.
All Comments (0)